What are the aspects of standardised information sharing?
GS1 uses identification keys to create globally recognisable, unique identifiers for every individual product. Most consumers recognise these keys as barcodes, but standardisation allows your business' unique barcodes to be read and recognised globally.
The most common GS1 identification keys for items in the meat industry fall under the category of GTIN, SSCC and application identifiers (AI).
Global Trade Identification Numbers (GTIN) are used by a company to uniquely identify all its trade items. This allows the item, along with its batch/lot number and expiry date to be identified anywhere in the world as your company’s product. A GTIN can be encoded in a barcode or RFID, allowing a streamlined process through your warehouse, to a retailer or exporter seamlessly, able to be understood throughout the supply chain.


Serial Shipping Container Codes (SSCC) are identifiers designed to be placed on pallets, crates, and other logistics units designed for storage or transport. They can be used to identify any combination of trade items within. An SSCC enables every logistics unit to be tracked and traced, and allows the recipient of the logistics unit to process it more easily.
Application Identifiers (AI) can be added to an identification key to give additional information to the product or unit. For example, the meat industry traditionally uses the AI 7002 to identify information about the quality of a cut or carcass for trade within the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe. They are also commonly used within Australia for the purpose of denoting weight, production date, batch/lot codes and expiry dates. AI are especially common for the packaging for major food retailers.
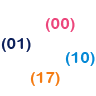

While the most commonly recognisable identification keys are barcodes, the GS1 DataMatrix is making its way into the public conscience, as more businesses are adopting it into their supply chains. A data matrix contains more character space then a barcode, making it more useful for the meat industry, which often needs to share a large amount of information in a small space on a carton or product. A data matrix is different from a QR code, in that QR codes have a reputation for being used for urls and other marketing, rather then strictly for information sharing. A data matrix is also capable of taking up to 40% surface damaged and still being readable, making it ideal for exporting and transporting goods.
What are the aspects of standardised information sharing?
GS1 uses identification keys to create globally recognisable, unique identifiers for every individual product. Most consumers recognise these keys as barcodes, but standardisation allows your business' unique barcodes to be read and recognised globally.
The most common GS1 identification keys for items in the meat industry fall under the category of GTIN, SSCC and application identifiers (AI).

Global Trade Identification Numbers (GTIN) are used by a company to uniquely identify all its trade items. This allows the item, along with its batch/lot number and expiry date to be identified anywhere in the world as your company’s product. A GTIN can be encoded in a barcode or RFID, allowing a streamlined process through your warehouse, to a retailer or exporter seamlessly, able to be understood throughout the supply chain.

Serial Shipping Container Codes (SSCC) are identifiers designed to be placed on pallets, crates, and other logistics units designed for storage or transport. They can be used to identify any combination of trade items within. An SSCC enables every logistics unit to be tracked and traced, and allows the recipient of the logistics unit to process it more easily.
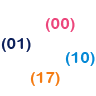
Application Identifiers (AI) can be added to an identification key to give additional information to the product or unit. For example, the meat industry traditionally uses the AI 7002 to identify information about the quality of a cut or carcass for trade within the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe. They are also commonly used within Australia for the purpose of denoting weight, production date, batch/lot codes and expiry dates. AI are especially common for the packaging for major food retailers.

While the most commonly recognisable identification keys are barcodes, the GS1 DataMatrix is making its way into the public conscience, as more businesses are adopting it into their supply chains. A data matrix contains more character space then a barcode, making it more useful for the meat industry, which often needs to share a large amount of information in a small space on a carton or product. A data matrix is different from a QR code, in that QR codes have a reputation for being used for urls and other marketing, rather then strictly for information sharing. A data matrix is also capable of taking up to 40% surface damaged and still being readable, making it ideal for exporting and transporting goods.

